The Table Access Protocol (TAP) service provides a standardized way, defined by the International Virtual Observatory Alliance (IVOA), to query the SBX catalogue using Astronomical Data Query Language (ADQL). This is a powerful tool for advanced users who need to perform complex searches and retrieve data programmatically.
In addition, you can access the TAP service endpoint and run your queries using various astronomy tools like TOPCAT, or through libraries like Astroquery in Python.
Run a Custom Query
Database Schema
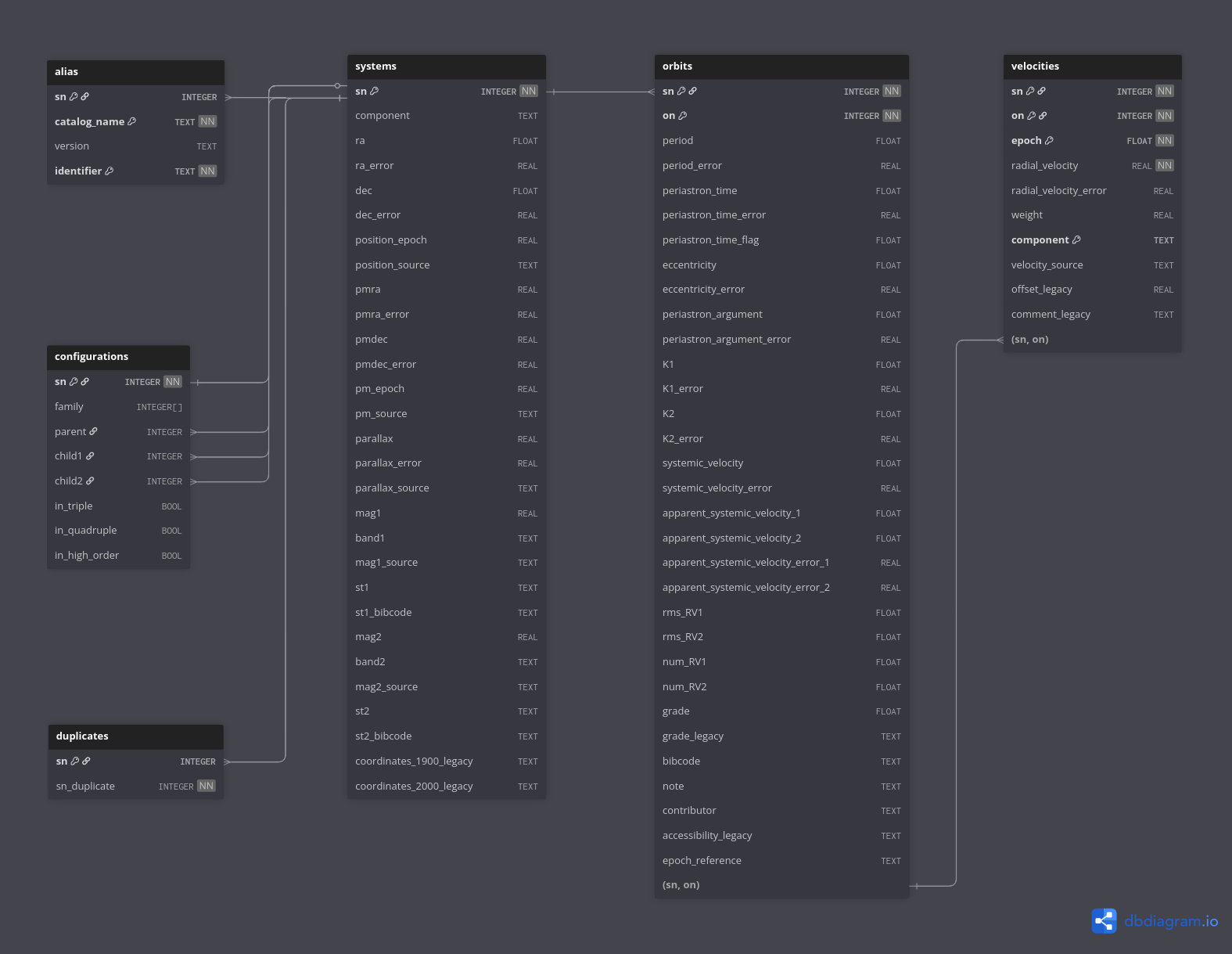
The SBX database is structured as a relational SQL schema comprising six main tables. The systems table contains core properties for each binary system, such as coordinates, proper motions, parallaxes, and magnitudes. The orbits table stores the orbital parameters. The velocities table records radial velocity measurements. The alias table maintains cross-identifications with external catalogues. The configurations table captures the hierarchical structure of multiple systems, and the duplicates table lists duplicate entries uncovered in SB9.
For a detailed description of the columns in each table, please refer to the TAP tables documentation .
ADQL Examples
Here are example queries to help you get started with the SBX TAP service:
Example 1: Find all SB2 in SBX and their associated Gaia DR3 Identifier when it exists.
SELECT DISTINCT 'SBX', o.sn AS sn, a.catalog, a.version, a.identifier
FROM orbits o LEFT JOIN alias a
ON o.sn = a.sn AND a.catalog = 'Gaia' AND a.version = 'DR3'
WHERE o.K1 IS NOT NULL AND o.K2 IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY sn;This query returns:
'SBX'| sn |catalog|version| identifier -----|----|-------|-------|--------------------- "SBX"|1 |"Gaia" |"DR3" |"2444348733779214976" "SBX"|4 | | | "SBX"|5 |"Gaia" |"DR3" |"2860078031611441152" "SBX"|6 |"Gaia" |"DR3" |"420596084197761920" "SBX"|10 |"Gaia" |"DR3" |"2752338227234710784" ...
To count the total number of such systems:
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT sn)
FROM orbits
WHERE K1 IS NOT NULL AND K2 IS NOT NULL;This returns the total count:
COUNT ------- 1366
Example 2: Find all Gaia DR3 identifiers of SBX binaries with periods and eccentricities, sorted by the brightness of the primaries.
SELECT sn, catalog, version, identifier, mag1, period, eccentricity
FROM orbits JOIN systems USING(sn) JOIN alias USING(sn)
WHERE catalog = 'Gaia' AND version = 'DR3'
ORDER BY mag1This query returns the following columns:
sn | catalog | version | identifier | mag1 | period | eccentricity -----|---------|---------|-----------------------|-----------|----------|-------------- 877 | Gaia | DR3 | 1220110705972528512 | 2.0 | 227.53 | 0.0 877 | Gaia | DR3 | 1220110705972528512 | 2.0 | 227.5687 | 0.0 21 | Gaia | DR3 | 4993479684438433792 | 2.0899775 | 3848.83 | 0.34 331 | Gaia | DR3 | 3220756843825383936 | 2.14 | 5.7325 | 0.087 331 | Gaia | DR3 | 3220756843825383936 | 2.14 | 5.7324 | 0.1 387 | Gaia | DR3 | 3377072212924335488 | 2.2620378 | 2983.0 | 0.53 ...
Example 3: Find spectroscopic binaries that are part of triple systems.
SELECT sn, ra, dec, mag1, family, parent, child1
FROM systems JOIN configurations USING(sn)
WHERE configurations.in_triple = 'True';This query returns:
sn | ra | dec | mag1 | family | parent | child1
-----|-------------------------|-------------------------|-----------|-------------|--------|--------
27 | 8.813855157623951 | -3.5929208153030223 | 5.0347004 | {27,2545} | 2545 | 27
49 | 14.195950792545961 | 60.3628186209266 | 5.967921 | {49,1726} | 1726 | 49
122 | 36.49170662112522 | 56.10276822633379 | 7.88 | {122,123} | 123 | 122
123 | 36.49170662112522 | 56.10276822633379 | 7.88 | {122,123} | 123 | 122
157 | 47.04221855625 | 40.95564667027778 | 2.12 | {157,158} | 158 | 157
158 | 47.04221855625 | 40.95564667027778 | 2.12 | {157,158} | 158 | 157
169 | 51.64763580350286 | 28.7146056635633 | 6.37 | {169,2464} | 2464 | 169
...
Example 4: Find all orbits referenced with individual RV data in SBX.
SELECT DISTINCT sn, o."on", bibcode, contributor
FROM orbits o
LEFT JOIN velocities v USING(sn)
WHERE v.sn IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY sn;This query returns:
sn | on | bibcode | contributor ----|----|-----------------------------------------------------|------------- 1 | 1 | 1926PDAO....3..341H | DAO 1 | 2 | 2024A&A...684A..74M | TMe 2 | 1 | 1975ApJ...200..122H | DAO 2 | 2 | 1999AstL...25..169B | PBX 4 | 1 | 1976PDAO...14..379A | DAO 4 | 2 | 2000A&AS..145..215P | PBX 4 | 3 | 1999A&A...351..963R | EVG 4 | 4 | 1995AJ....109..780T | EVG 5 | 1 | 1985JRASC..79...49H | DAO 5 | 2 | 1992A&AS...93..545M | LEITON ...